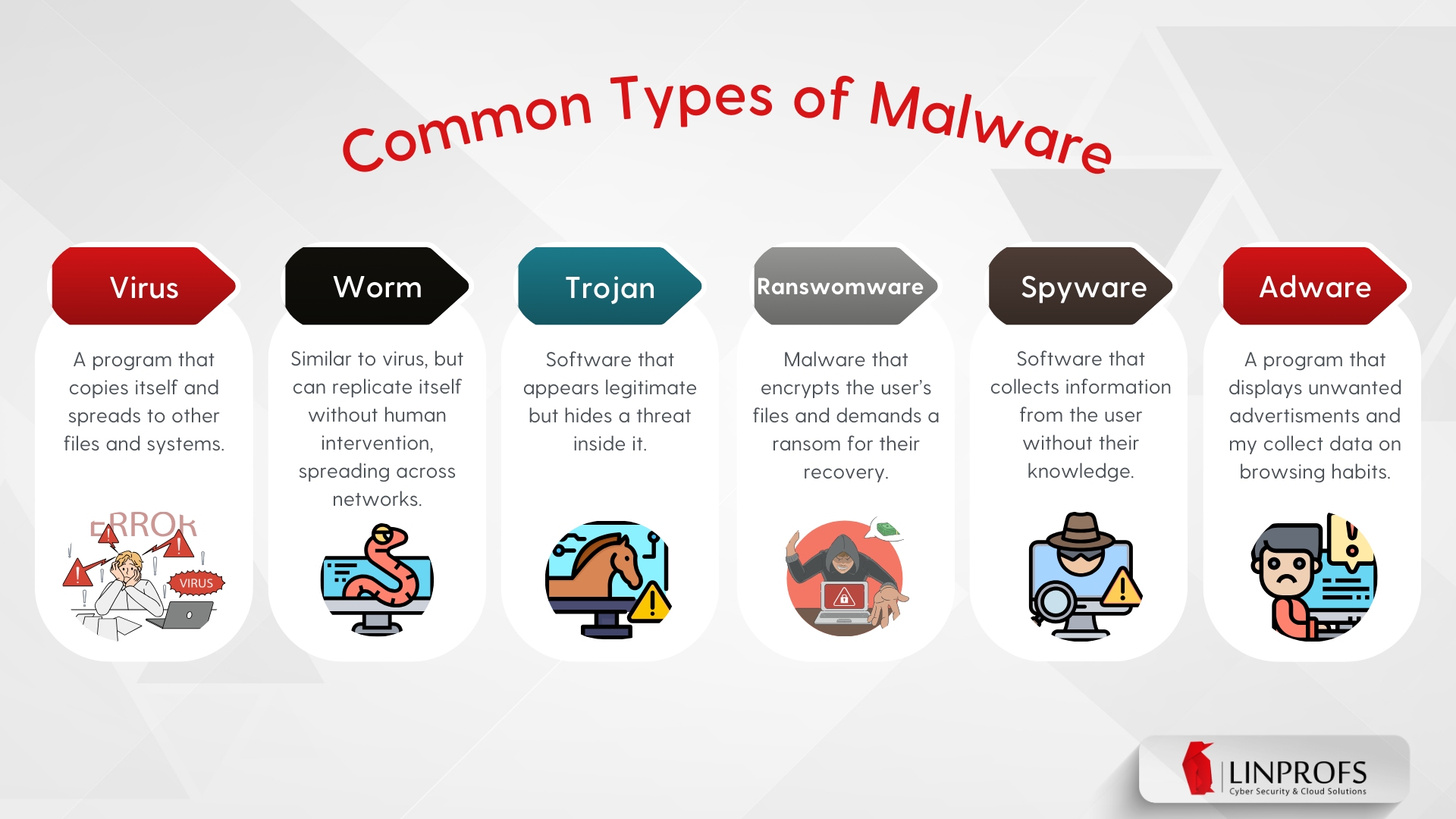
Malware (Malicious Software) refers to programs that damage computer equipment and/or extract information from users without their consent. In an ever-growing digital world, understanding the Malware is fundamental to protecting our data and system.
Do you know how Malware spreads?
One of the most common ways malware infiltrates systems is through phishing emails. These seemingly legitimate emails contain malicious links or attachments, tricking users into downloading infected software, especially from unverified or unofficial sources. This is why it’s crucial to only click or download from trusted links. But, no worries, in our upcoming articles, we’ll explore phishing in more detail, helping you understand why it’s important to recognize how phishing works and how you can protect yourself.
Social media and SMS have also become common ways of spreading malware. Cybercriminals often use these platforms to spread malicious links that compromise devices when clicked pretend being one of your friends, family, from your bank, etc. Another frequent source of infection is through external devices such as USB drives. Plugging a compromised device into your computer can introduce malware if proper security measures aren’t in place.
Given the wide range of malware delivery methods, it’s essential to stay vigilant and implement strong cybersecurity practices to protect your data and systems.
What are the consequences of Malware Attacks?
One of the most critical impacts is data loss, where essential files are deleted or encrypted, making them inaccessible. For organizations that depend on data for daily operations, this can be devastating.
In addition to losing data, malware often leads to theft of personal information. Cybercriminals can steal sensitive data, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or any other confidential business details, using this information for fraudulent activities. This puts both individuals and companies at high risk of identity theft and financial fraud.
A malware breach can severely harm a company’s reputation. Customers may lose trust in a business that fails to protect their personal data and rebuilding the trust after a breach can be very difficult. Reputation management is fundamental, and a single malware incident can compromise years of customer loyalty.
Finally, the financial impact of malware can be quite high. Beyond lost revenue due to system downtime or stolen assets, businesses often face significant costs related to data recovery, system restoration, and implementing preventive measures. Additionally, companies may face legal and regulatory penalties, making malware not just a cybersecurity issue but a financial and reputational crisis that demands immediate attention.
What steps can be taken to prevent Cyber Threats?
To protect against malware, it’s vital to implement robust security practices that minimize the risk of potential infection. One of the most important steps is keeping software up to date, installing the latest updates for operating systems, applications, and security tools. Many malware attacks exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software, so ensuring everything is current significantly reduces the risk of being targeted by cybercriminals.
Another essential measure in defending against malware is using reliable antivirus software. A robust security solution can detect, block, and remove malicious software before it causes harm. Antivirus programs are designed to scan files, monitor network traffic, and alert users when suspicious activity is detected, providing an additional layer of defense that can stop malware in its tracks.
However, technology alone isn’t enough. Educating users about the dangers of malware is equally important. Employees should be trained to recognize the signs of potential attacks, such as phishing emails with suspicious links, and understand the significance of practicing safe online behaviors. Human error is often a weak point in cybersecurity, and a well-informed workforce can be the first line of defense against malware. According to a study by IBM, human error is the main cause of 95% of cyber security breaches.
Finally, performing regular backups of important data is a key preventive strategy. In the event of a malware infection, particularly one involving ransomware, having up-to-date backups ensures that critical data can be restored without paying a ransom or losing valuable information. Backups should be stored securely and tested periodically to ensure they can be quickly accessed and deployed in case of an emergency.
By combining the practices mentioned earlier, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their chances of falling victim to malware attacks.
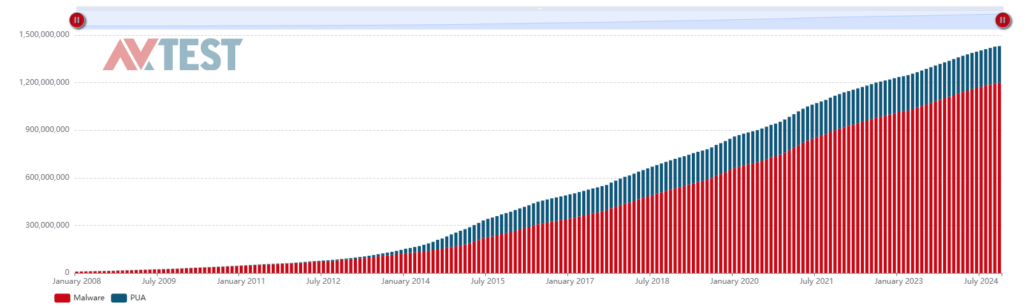
Malware is a constantly evolving threat that can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations alike. As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, the importance of proactive cybersecurity grows. Education, prevention, and a swift response are essential to minimizing the risks posed by malware. Training users to recognize threats, employing strong security tools, and having a well-defined response plan can significantly reduce the impact of an attack. Staying informed on the latest cybersecurity trends is crucial to staying ahead of new threats and protecting systems from evolving malware tactics.


Comments are closed